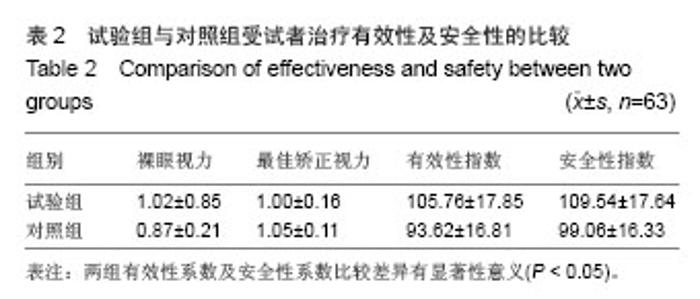
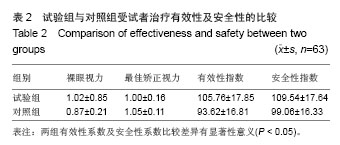
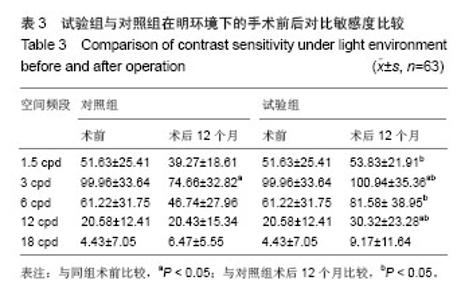
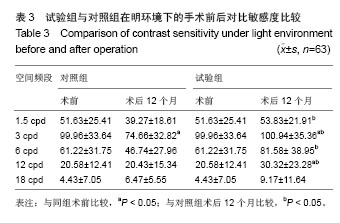
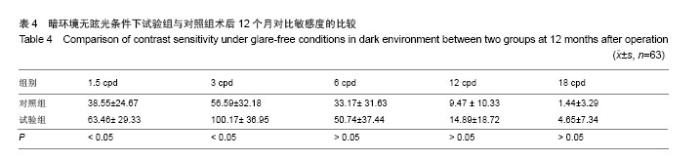
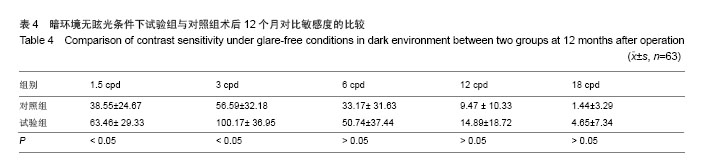
| [1]Rosman M,Alió JL,Ortiz D,et al.Comparison of LASIK and photorefractive keratectomy for myopia from-10.00 to-18.00 diopters 10 years after surger. J Refract Surg. 2010;26(3): 168-176.
[2]Padmanabhan P,Mrochen M,Viswanathan D,et al.Wave-front aberrations in eyes with decentered ablations.J Cataract Refract Surg.2009;35(4):695-702.
[3]何为兰.后房型人工晶体植入有晶体眼矫正高度近视12例的护理[J].中国误诊学杂志,2012,12(18):5188-5189.
[4]Kwon Y,Bott S.Postsurgery corneal asphericity and spherical aberration due to ablation efficiency reduction and corneal remodelling in refractive surgeries. Eye. 2009;23(9):1845-1850.
[5]Buzzonetti L,Petrocelli G,Valente P,et al.Comparison of corneal aberration changes after laser in situ keratomileusis performed with mechanical microkeratome and IntraLase fem-tosecond laser: 1- year follow - up. Cornea. 2008;27(2): 174-179.
[6]Villa C,Gutiérrez R,Jiménez JR,et al.Night vision dis-turbances after successful LASIK surgery.Br J Ophthalmol. 2007;91(8):1031-1037.
[7]Boxer Wachler BS,Scruggs RT,Yuen LH,et al.Comparison of the Visian ICL and Verisyse phakic intraocular lenses for myopia from 6.00 to 20.00 diopters.J Refract Surg. 2009; 25(9): 765-770.
[8]Kamiya K,Shimizu K,Aizawa D,et al.One-year follow-up of posterior chamber toric phakic intraocular lens implantation for moderate to high myopic astigmatism. Ophthalmology. 2010;117(12):2287-2294.
[9]Alfonso JF,Lisa C,Abdelhamid A,et al.Three-year follow-up of subjective vault following myopic implantable collamer lens implantation.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;248 (12):1827-1835.
[10]Rayner SA,Bhikoo R,Gray T.Spherical implantable collamer lenses for myopia and hyperopia: 126 eyes with 1-year follow up.Clin Experiment Ophthalmol.2010;38(1): 21-26.
[11]Chang J,Lau S.Toric Implantable Collamer Lens for high myopic astigmatic Asian eyes. Ophthalmology. 2009;116(12): 2340-2347.
[12]Emarah AM, El-Helw MA, Yassin HM. Comparison of clear lens extraction and collamer lens implantation in high myopia. Clin Ophthalmol.2010; 4: 447-454.
[13]Kojima T, Horai R,Hara S, et al. Correction of residual refractive error in pseudophakic eyes with the use of a secondary piggyback toricImplantable Collamer Lens. J Refract Surg. 2010; 26(10): 766-769.
[14]Kawamorita T, Uozato H, Shimizu K. Fluid dynamics simulation of aqueous humour in a posterior-chamber phakic intraocular lens with a central perforation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2012; 250(6): 935-939.
[15]Espandar L, Meyer JJ, Moshirfar M. Phakic intraocular lenses. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19(4):349-356.
[16]Dougherty PJ. Improving accuracy of phakic intraocular lens sizing using high-frequency ultrasound biomicroscopy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37(1): 13-18.
[17]Schmitz JW, McEwan GC, Hofmeister EM. Delayed presentation of traumatic dislocation of a Visian Implantable Collamer Lens. J Refract Surg. 2012; 28(5): 365-367.
[18]Mori T, Yokoyama S,Kojima T, et al. Factors affecting rotation of a posterior chamber collagen copolymer toric phakic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38(4): 568-573.
[19]Bhiko R, Rayner S, Gray T. Toric implantable collamer lens for patients with moderate to severe myopic astigmatism: 12-month follow-up. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2010; 38(5): 467-474.
[20]Camoriano GD, Aman-Ullah M,Purba MK, et al. Toric collagen copolymer phakic intraocular lens to correct myopic astigmatism in eyes with pellucid marginal degeneration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012; 38(2): 256-261.
[21]Hashemian SJ,Soleimani M,Foroutan A, et al. Toric implantable collamer lens for high myopic astigmatism in keratoconic patients after six months. Clin Exp Optom. 2013;96(2):225-232.
[22]Navas A, Tapia-Herrera G,Jaimes M, et al. Implantable collamer lenses after intracorneal ring segments for keratoconus. Int Ophthalmol. 2012;32(5):423-429.
[23]Alfonso JF, Lisa C,Fernandez-Vega Cueto L, et al. Comparison of visual andrefractive results of Toric Implantable Collamer Lens with bioptics for myopic astigmatism. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2013;251(3): 967-975.
[24]Saka N.Long-term changes in axial length in adult eyes with pathologic myopia.Am J Ophthalmol.2010;150(4): 562-568.
[25]张晓琳,范光忠,叶树波.LASIK术中应用飞秒激光制瓣的临床效果观察[J]中国实用医药, 2014,9(1):60-61.
[26]李雪瑶,张玙,晏丕松,等.LASIK治疗近视行飞秒激光与角膜刀制瓣术后视觉效果Meta分析[J].中国实用眼科杂志, 2014,32(5): 607-615.
[27]荣运久,王菲,刘菲,等.ICL或TICL植入术临床矫治高度近视[J].实用医药杂志,2013,30(1):11-13.
[28]霍永军.有晶状体眼后房型人工晶状体植入矫正高度近视的临床观察[J].河南外科学杂志,2013,19(5):31-33.
[29]魏静,吴杰,罗斌,等.有晶体眼后房型人工晶体植入术治疗超高度近视的临床观察[J]. 航空航天医学杂志,2013,24(2):131-133.
[30]吴燕,罗涛,蒋炜,等.有晶体眼后房型人工晶体植入术早期并发症观察及其处理[J].局解手术学杂志,2014,23(2):182-184.
[31]李毅,徐宇红,王珂.有晶状体眼后房型人工晶体植入术治疗高度近视手术的护理[J].实用临床医药杂志,2014,18(4):99-100.
[32]Cosar CB,Gonen T,Moray M,et al.Comparison of visual acuity, refractive results and complications of femtosecond laser with mechanical microkeratome in LASIK.Int J Ophthalmol. 2013;6(3):350-355.
[33]胡春明,罗启惠,熊洁,等.有晶状体眼后房型散光性人工晶体植入矫治复性超高度近视散光[J].第三军医大学学报, 2014,36(1): 81-84.
[34]Torun N,Bertelmann E,Klamann MK,et al.Posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens to correct myopia: long-term follow-up. J Cataract Refract Surg.2013;39(7):1023-1028.
[35]Alfonso JF,Baamonde B,Madrid Costa D,et al.Collagen copolymer toric posterior chamber phakic intraocular lenses to correct high myopic astigmatism.J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36(8):1349-1357.
[36]周天安,沈晔,汪阳,等.有晶状体眼后房型人工晶状体植入矫正高度近视的中远期疗效评价[J].中华眼科杂志,2012,35(4): 307-311.
[37]Kamiya K,Shimizu K,Igarashi A.Four-year follow- up of posterior chamber phakic intraocular lens implantation for moderate to high myopia.Arch Ophthalmol.2009;127 (7): 845-850.
[38]Blum M,Kunert KS,Engelbrecht C,et al.Femtosecond Lenticule Extraction (FLEx)- Results after 12 Months in Myopic Astigmatism.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2010;227(12): 961-965.
[39]Dong Z,Wang NL,Li JH.Vision subjective accommodation and lens mobility after TetraFlex accommodative intraocular lens implantation.Chin Med J (Engl).2010;123(16):2221-2224.
[40]Von Mohrenfels CW,Salgado J,Khoramnia R,et al.Clinical results with the light adjustable intraocular lens after cataract surgery.Refract Surg.2010;26(5):314-320. |